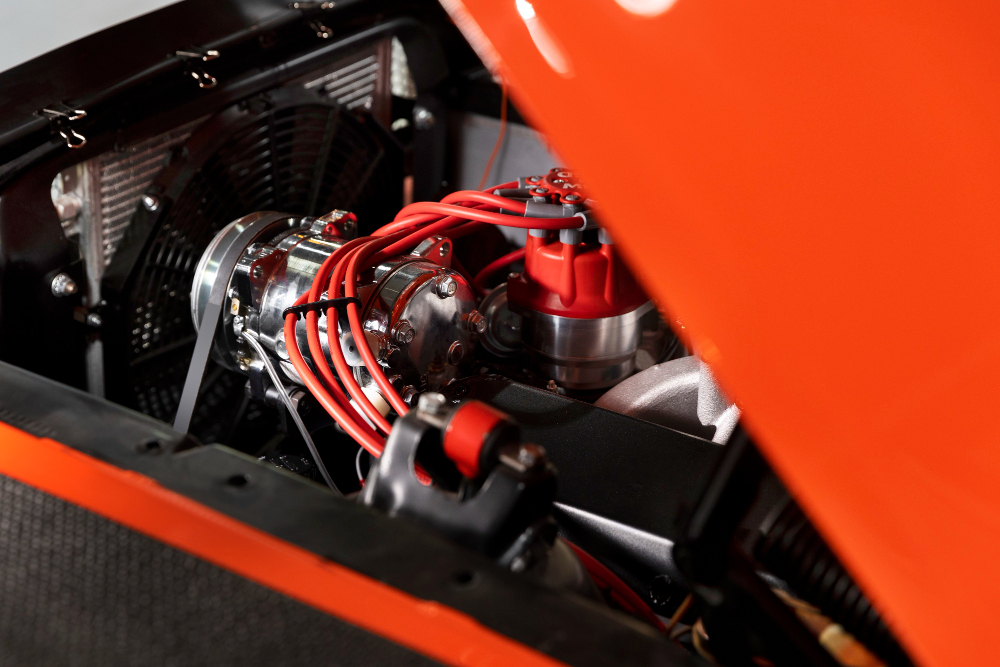
A twin-turbo engine is distinct from the twincharger setup, which combines a supercharger and a turbocharger. This twin-turbo engine compresses the intake fuel-air mixture or direct injection air with two turbochargers working as one system. The layout commonly features parallel identical or mirrored turbos managing half of each cylinder’s exhaust through individual piping systems. This pair of turbines can either be matching sizes or different measurements for varying performance results.
What Does Twin Turbo Mean?
The word ‘Turbo’ can easily be placed onto several products, leaving one with the assumption that it is going to perform swiftly and powerfully. After all, turbo blenders and vacuum cleaners are always presented as fast-acting devices; however, when applied to cars, things get serious very quickly.
Doubles Efficiency
A turbocharged engine doubles its efficiency when it has not one but two turbos! These twinned-up forces of power can be either identical or dissimilar; moreover, their placement and installation differ in various vehicles.
More Power
Twin-turbo engines have become increasingly sought after for a good reason: they provide incredible power with just four cylinders instead of the eight required by single turbo models. Furthermore, their dual turbos minimize lag time and deliver maximum performance – whether cruising down city roads or traversing open highways. These engines offer reliable speed and efficiency for any regular driver, making them an ideal choice.
Cost-Efficient Performance
Twin-turbo guarantees a seamless running engine. Economically speaking, two smaller turbochargers are more cost-efficient than one larger one. Nevertheless, some engines necessitate twin-turbo kits to ensure optimal performance and efficiency, specifically in the case of V-type engines that run better with this system installed. However, it is crucial to be aware of the drawbacks associated with opting for a twin over a single turbo – its need for extra space and additional fees during installation.
Principle of Twin Turbo
The turbo is an intricate assembly comprising two primary components: the turbine and compressor wheels, bound together by a single shaft. This mechanical structure is packed within a shell shaped like a snail having both inlet and exhaust ports. Essentially, when the engine releases hot exhaust gases through the inlet port at high pressure, it spins the turbine wheel, which simultaneously drives the rotation of the compressor wheel that draws significant volumes of air and forces them out from its outlet port after compressing them to higher pressures.
Pipe and Intercooler
Compressed air is delivered to the cylinders through a pipe and an intercooler that cools off hot exhaust gases before they reach the cylinders. To protect against rapid rotational speed, turbo systems typically feature oil cooling and a wastegate valve, which prevents damage by diverting excessive exhaust from the turbine.
A turbocharged engine functions similarly to a regular internal combustion engine; the only distinction is its increased power and efficiency, obtained from compressed air fed by the turbocharger.
Same Size Turbochargers
The power of a twin-turbocharger is harnessed by utilizing two turbochargers that are the same size. These turbochargers recycle exhaust gases and force them into an engine’s cylinders, resulting in extra horsepower. This method is known as a parallel twin-turbo system since it combines two turbos with a shared inlet before entering cylinders; this intensifies the amount of air being induced into the induction chamber, leading to increasingly powerful combustion strokes.
V Engines

Twin turbos are commonly found on V engines that possess two exhaust ports. Normally, these turbines are positioned at the sides of the engine bay except in cases where a hot V configuration is employed, thus placing them inside the motor valley. Using dual turbochargers, smaller turbines can be adopted, which widens the power band and enhances low-end torque thanks to its lower boosting threshold.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Twin Turbo
Many car owners opt to have twin-turbo engines in their vehicles. Even though this system is more expensive than single turbo systems, it has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Twin Turbo
Here are the advantages of a twin-turbo engine in your car.
- More Power – The advantages of twin-turbo engines are that they provide better power than single turbos, require less space to install due to their smaller size, and have a broad powerband. Fuel economy is also improved as the turbochargers work in tandem with each other.
- Efficient Engine Functionality – Twin-turbo is an excellent method for ensuring even engine functionality. This system is more efficient than one large turbocharger because its two smaller ones require less expense in the long run. Nevertheless, some engines will benefit from twin-turbo kits when paired with V-type motors as they work together intuitively and effectively.
- Reduced Lag Time – Taking advantage of a twin-turbo setup provides the added benefit of reduced lag time. This powerful engine utilizes four cylinders to provide faster power than a single turbo that needs all eight cylinders for optimal performance. If you are looking for an efficient car for regular city driving or routine running, this type of system is your best option.
Disadvantages of Twin Turbo
Here are the disadvantages of using a twin-turbo engine in a car.
- More space Needed – Twin-turbo setups require more space in the engine bay, which can be a disadvantage for some car owners. Since it requires two separate turbochargers, extra space for installation is a must. Additionally, some automakers may require special parts and additional charges when opting for this setup.
- Higher Installation Costs – Installing two turbos in one car costs more than installing a single turbocharged system. Although it provides better power and efficiency than its single-turbo counterpart, the cost of the two turbos and their installation can be a bit pricey.
- High Maintenance – Twin-turbo engines also require higher maintenance than standard setups since they need two turbos with different upkeep requirements. Additionally, the inter-connected tubing of two turbines can lower efficiency over time if not regularly cleaned and maintained.
Overall, twin-turbo engines are a great way to maximize power and efficiency in your car. However, it is essential to consider the costs, space requirements, and maintenance needs before going for this type of setup. After weighing all the factors, you can decide whether or not investing in a twin-turbo engine is worth it.
Twin Turbo in Different Engines
In the automotive world, turbo engines are increasingly becoming a sought-after item due to their efficiency and capability of creating power without any extra energy draw. Compared to other methods, such as superchargers, turbos cause no parasitic drag, making them an even more attractive choice for many drivers.
Here are the three main types of twin-turbo setups.
Parallel Twin-Turbo Setup
Parallel twin turbo systems are the most efficient and cost-effective choice for engine bays due to their compact size and minimal exhaust piping. Additionally, smaller turbos can be used instead of one large one, which reduces the lag at lower revs compared to larger single turbos that generally require more time to spool up. That said, some level of turbine lag will still exist until these tiny turbines have had a chance to power up fully.
The earliest form of twin turbocharging and the most basic configuration in exhaust piping is found in V-shaped engines, such as the V6, V8, V10, and V12. This parallel setup has two identical turbochargers that feed their power to each bank cylinder separately. But it’s best to use a single turbo setup for inline layouts.
Sequential Twin-Turbo Setup
To avoid lag issues, a sequential twin-turbocharged design often employs two turbos in tandem: a smaller one that provides rapid response at lower speeds and helps the bigger one “spin up” with more exhaust flow; and a larger unit to generate maximum power when revs are high. This combo delivers instant acceleration while giving you the power of both engines for sustained performance.
Sequential turbochargers are often utilized to bridge the gap between superior power and responsive agility. However, their complexity can lead to increased maintenance requirements and reliability issues. But when set at a factory-determined switchover point or high rpm levels, a higher boost is achievable without any detectable lag as workloads are transferred from one small turbo to another larger one.
Additionally, perfectly adjusting the settings for a custom tuner with two turbochargers (small and large) can be rather pricey. It’s no wonder many car enthusiasts opt for the more straightforward option of upgrading to just one larger turbo.
Series Twin-Turbo Setup
Serial turbocharging involves using two or more consecutively arranged turbochargers, with the output of the first then fed into and further compressed by the second. In some cases, this process can even power a larger turbine. A series twin-turbo engine is designed to deliver a massive power boost by setting up two turbochargers in sequence. The output from the first turbo is further compressed by the second one, creating an immense pressure buildup with impressive results.
Staged turbocharging is a multi-step procedure that uses two or more turbos to create exceptionally high levels of air compression before the engine’s cylinders. This system starts with one smaller and relatively lag-free turbine. Then it funnels the compressed air through an even larger turbo for greater boost pressure, allowing diesel engines with low rev ranges and higher compression ratios to enjoy superior power output than standard twin-turbo systems. However, this comes at a cost — as desired performance increases, so does the dreaded “lag” factor!
Things to Consider Before Turbocharging a Car
Turbocharging a car can be both a fun and rewarding experience. It can add power, performance, and style to your vehicle – all at the same time. However, before installing a turbo system, several factors should be considered. Here are a few of them:
Installation Cost
The installation cost is probably the most critical factor when considering whether or not to install a turbocharger. The cost of the parts and labor required can vary greatly depending on the type of car, engine size, and desired performance.
Reliability
A turbocharged engine is more powerful than an unmodified one; however, it also requires more significant upkeep to remain reliable. It is important to consider how often you will need to perform maintenance, as well as the potential for any malfunctions that could occur.
Fuel Economy
Turbocharged engines are typically more efficient than non-turbocharged ones, so it is essential to factor in fuel economy when deciding whether or not to install a turbocharger. It may be worth sacrificing a bit of power to gain more miles per gallon.
Engine Readiness
The engine should also be ready to handle the increased power due to the turbocharge kit. It is crucial to verify that any necessary upgrades, such as high-performance spark plugs or upgraded fuel injection systems, are in place before attempting to install a turbocharger.
Other Components
The clutch, differential, transmission, and driveshafts should be checked to ensure they are in good condition and capable of handling the extra power. Also, proper tuning is essential for a smooth ride and optimal performance; hence, talking with an experienced expert before attempting any modifications is critical.
Work with a Professional

Lastly, it is best to install the turbocharger kit by a professional mechanic. A qualified technician will understand how to install the components and ensure everything works properly. This will ensure a smooth driving experience and keep your engine running in top form for years to come!
Twin-turbo systems are an increasingly popular choice for car owners who want to maximize power and efficiency without sacrificing too much space or money. With a parallel twin-turbo setup, two identical turbos can be used in the engine bay, providing better power than one single turbo with less expense. Sequential twins utilize two turbos to reduce lag time, while series twins use multiple consecutively arranged turbines for maximum boost pressure. Before investing in a twin-turbo system, it is essential to consider installation cost, reliability, fuel economy, engine readiness, and other components and enlist professional mechanics’ help. Ultimately, if you’re looking to add more horsepower and performance without compromising on fuel efficiency or size constraints, then a twin-turbocharged system might just be the perfect fit for your vehicle!






